Philippines
BACKGROUND
The Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines
The Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines (IPOPHL) is the lead agency in the country mandated to implement State Policies on intellectual property (IP). It was created by Republic Act No. 8293 or the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines (IP Code), which was signed into law on June 6, 1997 and took effect on January 1, 1998.
Mandate & Functions:
- Promote the use of patent information as a tool for technological development;
- Examine applications and grant patents, or register utility models, industrial designs, trademarks, geographical indication, and integrated circuits;
- Help protect copyright by assisting in the facilitation of deposit of work with the National Library
- Register technology transfer arrangements;
- Undertake enforcement functions supported by concerned agencies such as the PNP, NBI, Customs, OMB, LGUs, etc.;
- Conduct visits during reasonable hours to establishments and businesses engaging in activities violating IPRs and provisions of the IP Code based on report, information or complaint received by the Office;
- Hear and decide cases relating to violations of IP Rights;
- Cancellations and oppositions to registration;
- Compulsory licensing;
- Settle disputes involving technology transfer payments;
- Coordinate with relevant government agencies and the private sector efforts to formulate and implement plans and policies to strengthen the protection of intellectual property rights in the country;
- Develop and implement strategies to promote and facilitate technology transfer;
- Institutionalize its Copyright Services and create a Bureau of Copyright;
- Undertake enforcement function supported by other concerned government agencies; conduct visits to businesses and establishments engaging in activities violating IPR, based on report, information or complaint received by the Office; and
- Such other functions in furtherance of protecting IP rights and the objectives of the IP Code of the Philippines
Vision
An Intellectual Property-conscious Philippines in a demystified, development-oriented, and democratized IP System by 2020.
Mission
We commit to deliver high quality, fast, reliable, effective and efficient services to promote innovation and encourage the creation, utilization, protection of and respect for intellectual property.
Strategic and Management Goals
STRATEGIC GOALS
- Deliver quality and timely patents, trademarks, and other IP registrations;
- Provide effective enforcement and speedy and high quality adjudication mechanisms for the resolution of IP disputes that can be relied upon by all stakeholders;
- Provide mechanisms to support Filipino creators and innovators from creation to commercialization;
- Increase the level of awareness, appreciation, and respect for IP;
- Lead in the development of a fair copyright system that addresses the needs of all stakeholders;
- Provide the legal and policy infrastructure to address emerging national and global demands of the IP system; and
- Integrate intellectual property in the whole of society
MANAGEMENT GOALS
- Achieve institutional excellence by investing in people, technology, and infrastructure
- Develop and nurture a culture of excellence, deep commitment, and integrity
ORGANIZATION
The Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines is headed by the Director General and is assisted by two (2) Deputies Director General. At present, the Office has six (6) Bureaus, namely: the Bureau of Patents, Bureau of Trademarks, Bureau of Legal Affairs, the Documentation, Information and Technology Transfer Bureau, the Management Information Systems Bureau, and the Financial Management and Administrative Services Bureau. Each Bureau is headed by a Director and is assisted by an Assistant Director.
* Please note that with the Amendment under Republic Act No. 10372, another bureau, Bureau of Copyright will be established.

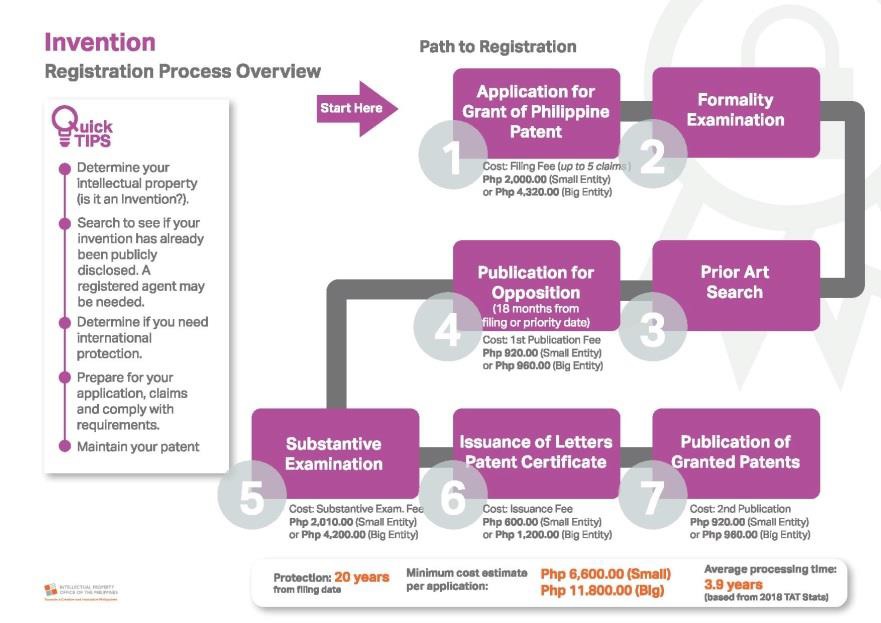
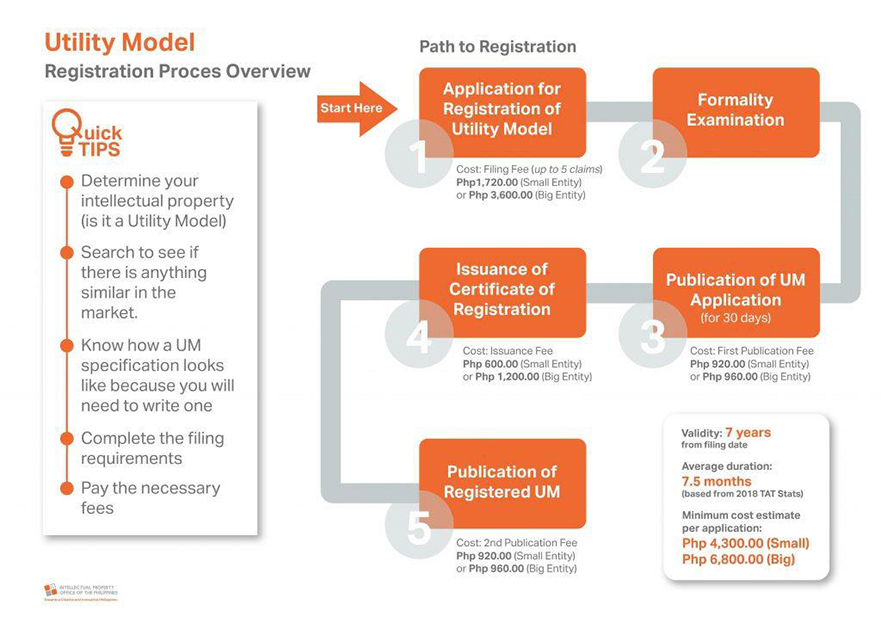
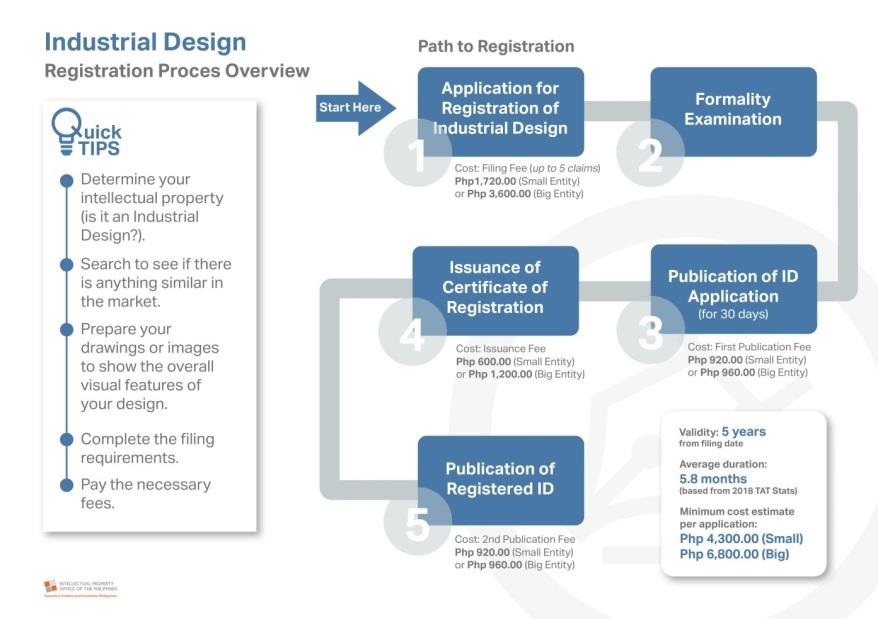
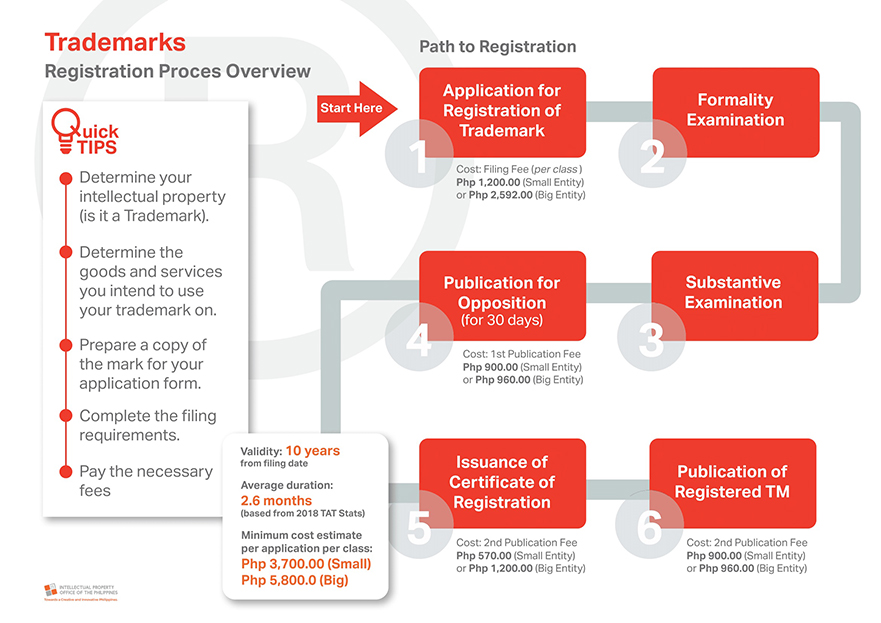
REGISTRATION PROCEDURE
LAWS AND REGULATIONS
| QUICK ACCESS | |||
| Laws (34 texts) | Implementing Rules/Regulations (41 texts) | Pending IP legislations |  |
| Treaty Membership (51 texts) | Relevant links | ||
Relevant links |
