Myanmar
BACKGROUND

Background
Myanmar is the largest country in mainland South-East Asia with a total land area of 676,578 square kilometers. It stretches 2200 kilometers from north to south and 925 kilometers from east-west at its widest point. Lying between 09'32’ N and 28'31’N latitudes and 92'10’ E and 101'11’ E longitudes, it is bounded on the north and north-east by the People’s Republic of China, on the east and southeast by the Lao People’s Democratic Republic and the Kingdom of Thailand, on the west and south by the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea, on the west by the People’s Republic of Bangladesh and the Republic of India. Myanmar became a founder country of the World Trade Organization (WTO) on 16th, November, 1994. Myanmar joined to ASEAN on 23rd July, 1997 and also became a 176th member country of WIPO on 15th May, 2001. As a member of WTO, WIPO and ASEAN, we have to abide the obligation of TRIPs Agreement and ASEAN Framework Agreement on IP CO-operation. In the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Judicial and Legal system on IPRs had timely developed at the early of 19th Century. The existing laws related to IP in Myanmar, which are Myanmar Patents and Designs Act of 1945 and Myanmar Patents and Designs (Emergency Provision) Act 1946 were promulgated but they are defunct and not active.
Myanmar became a founder country of the World Trade Organization (WTO) on 16th, November, 1994. Myanmar joined to ASEAN on 23rd July, 1997 and also became a 176th member country of WIPO on 15th May, 2001. As a member of WTO, WIPO and ASEAN, we have to abide the obligation of TRIPs Agreement and ASEAN Framework Agreement on IP CO-operation. In the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Judicial and Legal system on IPRs had timely developed at the early of 19th Century. The existing laws related to IP in Myanmar, which are Myanmar Patents and Designs Act of 1945 and Myanmar Patents and Designs (Emergency Provision) Act 1946 were promulgated but they are defunct and not active.
Concerning the Trademarks system, Myanmar do not have any Act like Trademarks Registration Act and no specific statutory law on trademarks and no statutory provision regarding registration of trademarks. However, the existing laws of Myanmar Merchandise Marks Act, Registration Act, Sea Custom and Land Custom Act and Penal Code (478) are in current use and there are relevant laws of Myanmar trademark system.
Regarding with Copyright Protection, the existing Myanmar Copyright Act was promulgated on 24th February, 1914 and it contains only 13 sections with Copyright Act 1911 act of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
These existing laws of Myanmar relating to Intellectual Property do not cope with the current economic trend and development in the field of Intellectual Property. As a member of the WTO and WIPO, Myanmar has an obligation to put in place the intellectual property laws with the minimum international standards protection. Apart from the TRIPs Agreement, Myanmar deeply considered the main objective of ASEAN Framework Agreement that the members must ensure the Intellectual Property Laws and practices in the ASEAN countries will not obstruct the free flow of literary and artistic works, goods and services throughout the ASEAN region but will promote and facilitate such an exchange.
Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) is a focal Ministry of WIPO since 2001 and responsible for the promotion of IP System in Myanmar. Ministry of Science and Technology and Attorney General Office (AGO) have worked together for drafting the IP Laws such as Patent, Industrial Design, Trademark and Copyright in accordance with TRIPs Agreement and with the major objective in order to facilitate access of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar to international markets and promote free trade and foreign direct investment. At the present stage, these draft IP laws are under the legislation process.
The Role of Ministry of Science and Technology

In order to enhance the development of Science and Technology and to reinforce the State Development more effectively the State Law and Order Restoration Council has established the Ministry of Science and Technology according to the declaration No.33/96 on the 2nd October. Ministry of Science and Technology is a focal Ministry takes responsibility for promotion of new IP systems to be in line with the International conventions and agreements including TRIPS agreement. The Ministerial office locates in building (21), Nay Pyi Taw.
The Objectives :
- To carry out Research and Development works for the national economic development
- To utilize the national resources so as to develop the economy, and raise the living standard of the people.
- To disseminate the technological know-how achieved from the Research and Development works to the industrial and agricultural sectors in order to enhance the production
- To plan and carry out human resources development programs so as to obtain specialists and professionals in Science and Technology
- To analyze and test raw materials and finished products, and to implement quality control and standardization of industrial products.
- To coordinate research, development and use of Atomic Energy.
The implementation programmes of the MOST are divided into two sectors:
- Developing Human Resource Sector
- Research and Development Sector
It has been carrying out the tasks concerning developing human resources to fullfill the increasing demand of industries, to conduct courses on new academic fields in order to meet the needs of current situation, to enable qualified students to pursue advanced technologies, and to disseminate technological know-how for the entire nation.
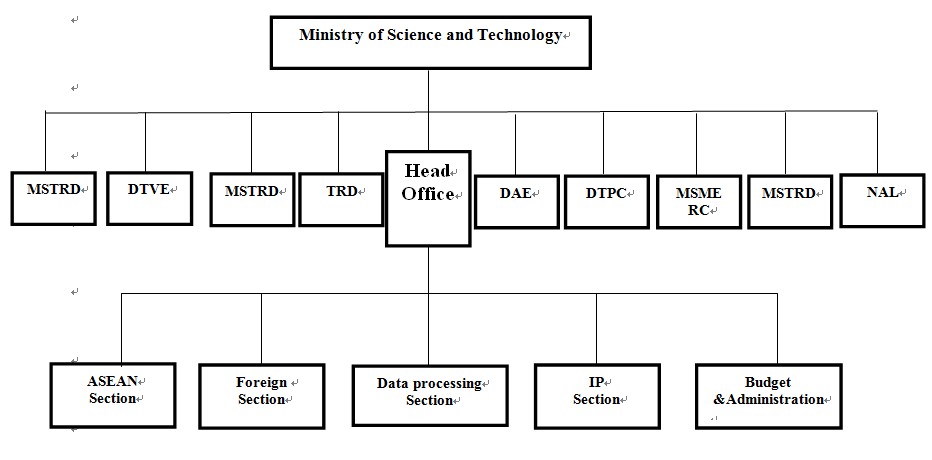
ORGANIZATION
Departments of MOST
Ministry of Science and Technology carry out the development of Science and Technology for promotion of industrial production contributory towards the National Economic Development plans.With the aim of enhancing successful implementation of development programmes in Science and Technology, the Ministry of Science and Technology was established on 2nd October 1996.
The Ministry of Science and Technology is organized with the following departments:
Organization Chart
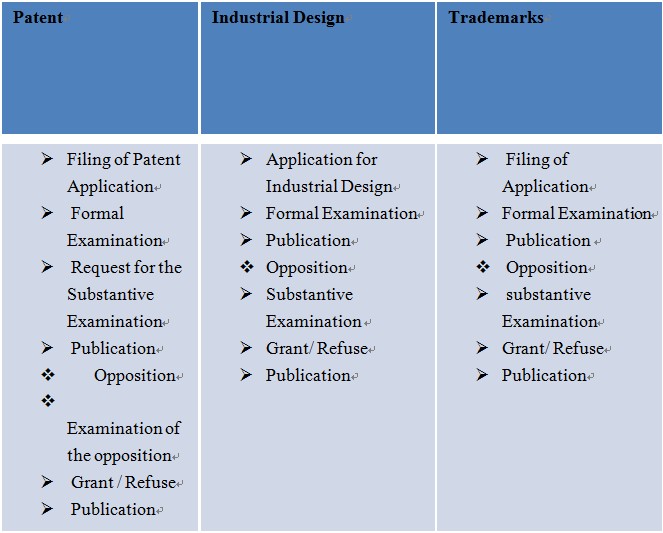
REGISTRATION PROCEDURE
LAWS AND REGULATIONS
| Quick Access | |||
| Laws (20 texts) | Implementing Rules/Regulations (1 texts) | Pending IP legislations |  |
| Treaty Membership (25 texts) | Relevant links | ||
Implementing Rules/Regulations |
Intellectual Property (Date of current version) |
Relevant links |
